Histogram Plots for all Elements and many compounds in NIST BEs
Examples of Histogram Plots
| Silver Metal, Ag | Gold Metal, Au | Copper Metal, Cu |
|
|
|
|
Histogram Plots Reveal Validity and Reliability,
and produce useful “Mean BEs” Values
BEs listed in the NIST database were collected over many years time by many different analysts operating many different XPS instruments who used:
- different BE Calibration Values
- Cu (2p3/2) BE ranged from 932.2 eV to 932.8 eV (a 0.6 eV range)
- different Separation in Calibration Values (SCE)
- separation values between Cu (2p3/2) and Au (4f7/2) ranged from 848.0 eV to 849 eV (a 1.0 eV range)
- different Carbon (1s) BEs for hydrocarbon type adventitious carbon
- C (1s) BE ranged from 284.2 eV to 285.2 eV (a 1 eV range)
- different frequency to check BE Calibration Values, or never checked
Therefore, some of the BE values from pure conductive elements have large BE ranges, as large as 1 eV. Non-conductive chemical compounds have much larger BE uncertainties because C (1s) was used to charge reference non-conductors, and also due to differential charging effects. Due to the use of different Cu (2p3/2) BEs for calibration at the high BE end, you will find increasing larger errors or uncertainties in BEs above 600 eV due to the ever increasing scaling difference as you go from o eV to 1,480 eV.
Recommend: Use NIST BEs as a Guide
Ag (Silver)


Ag (Silver)
Al (Aluminum)


Al (Aluminum)
Ar (Argon)

Ar (Argon)
As (Arsenic)




As (Arsenic)
Au (Gold)

Au (Gold)
B (Boron)



B (Boron)
Ba (Barium)


Ba (Barium)
Be (Beryllium)

Be (Beryllium)
Bi (Bismuth)


Bi (Bismuth)
Br (Bromine)

Br (Bromine)
C (Carbon)



C (Carbon)
Ca (Calcium)


Ca (Calcium)
Cd (Cadmium)




Cd (Cadmium)
Ce (Cerium)

Ce (Cerium)
Cl (Chlorine)


Cl (Chlorine)
Co (Cobalt)



Co (Cobalt)
Cr (Chromium)



Cr (Chromium)
Cs (Cesium)


Cs (Cesium)
Cu (Copper)







Cu (Copper)
Eu (Europium)

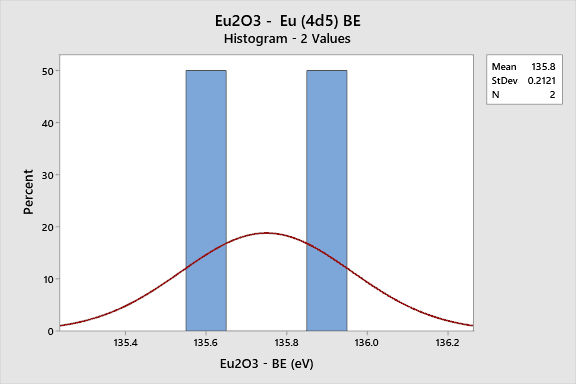
Eu (Europium)
F (Fluorine)



F (Fluorine)
Fe (Iron)





Fe (Iron)
Ga (Gallium)



Ga (Gallium)
Gd (Gadolinium)


Gd (Gadolinium)
Ge (Germanium)

Ge (Germanium)
Hf (Hafnium)

Hf (Hafnium)
Hg (Mercury)


Hg (Mercury)
Ho (Holmium)

Ho (Holmium)
I (Iodine)


I (Iodine)
In (Indium)


In (Indium)
Ir (Iridium)


Ir (Iridium)
K (Potassium)

K (Potassium)
La (Lanthanum)


La (Lanthanum)
Li (Lithium)



Li (Lithium)
Lu (Lutetium)


Lu (Lutetium)
Mg (Magnesium)


Mg (Magnesium)
Mn (Manganese)





Mn (Manganese)
Mo (Molybdenum)



Mo (Molybdenum)
N (Nitrogen)







N (Nitrogen)
Na (Sodium)


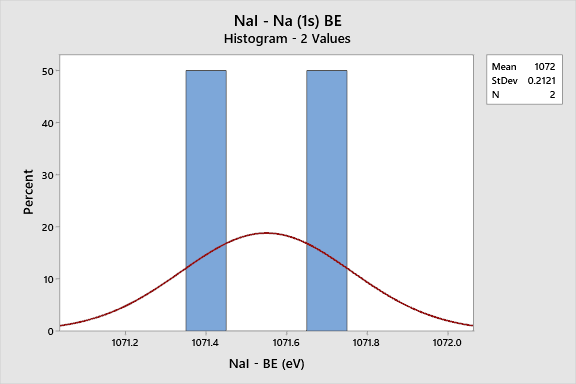

Na (Sodium)
Nb (Niobium)




Nb (Niobium)
Ne (Neon)

Ne (Neon)
Ni (Nickel)



Ni (Nickel)
O (Oxygen)






O (Oxygen)
Os (Osmium)


Os (Osmium)
P (Phosphorus)






P (Phosphorus)
Pb (Lead)




Pb (Lead)
Pd (Palladium)



Pd (Palladium)
Pt (Platinum)



Pt (Platinum)
Rb (Rubidium)

Rb (Rubidium)
Re (Rhenium)

Re (Rhenium)
Rh (Rhodium)


Rh (Rhodium)
Ru (Ruthenium)


Ru (Ruthenium)
S (Sulfur)




S (Sulfur)
Sb (Antimony)


Sb (Antimony)
Sc (Scandium)


Sc (Scandium)
Se (Selenium)

Se (Selenium)
Si (Silicon)





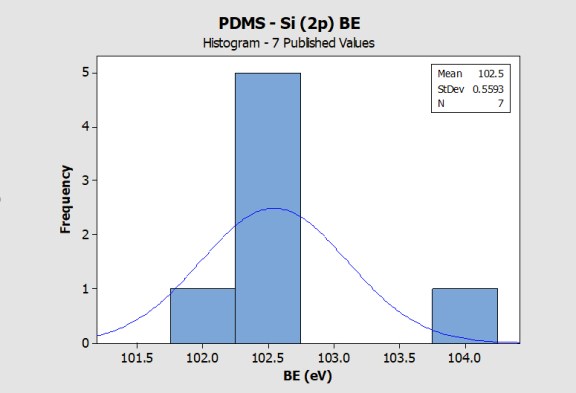
Si (Silicon)
Sn (Tin)



Sn (Tin)
Sr (Strontium)


Sr (Strontium)
Ta (Tantalum)


Ta (Tantalum)
Te (Tellurium)



Te (Tellurium)
Th (Thorium)

Th (Thorium)
Ti (Titanium)


Ti (Titanium)
Tl (Thallium)

Tl (Thallium)
U (Uranium)

U (Uranium)

U (Uranium)
V (Vanadium)


V (Vanadium)
W (Tungsten)




W (Tungsten)
Xe (Xenon)

Xe (Xenon)
Y (Yttrium)


Y (Yttrium)
Yb (Ytterbium)

Yb (Ytterbium)
Zn (Zinc)


Zn (Zinc)
Zr (Zirconium)


Zr (Zirconium)





