Summaries of BEs in NIST Database
- This collection of BE tables was compiled by M. Biesinger (UWO) by summarizing the BEs listed in the NIST XPS Database of BEs.
- Please review and evaluate the Standard Deviation (Std. Dev.) value when you are using any of these BEs to make any chemical state assignment.
- Large “Std. Dev.” values having only a few # of Reference citings are risky to use and may lead to wrong assignments, decisions and errors. Be careful please. Many researchers depend on your chemical state assignments to be accurate!
- Because the original researcher used C (1s) BEs that could be 284.6 eV, 284.8 eV, or 285.0 eV, the BEs for insulators might vary by as much as 0.4 eV.
- Older publications used different calibration energies for the Cu 2p3/2 BE: 932.2 eV, 932.47 eV, or 932.8 eV. This means that BEs above 500 eV can vary by as much as 0.6 eV for both insulators and conductors.
- The accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of these BEs depends on the efforts used by the original researchers. To learn more, please visit the NIST link in the main menu.
Aluminum, (Al)
Al (2p3/2) BEs
Antimony, (Sb)
Sb (3d5/2) BEs

Argon, (Ar)
Arsenic, (As)
As (3d5/2) BEs

Barium, (Ba)
Ba (3d5/2) BEs

Beryllium, (Be)
Be (1s) BEs

Bismuth, (Bi)
Bi (4f7/2) BEs

Boron, (B)
B (1s) BEs

Bromine, (Br)
Br (3d5/2) BEs

Cadmium, (Cd)
Cd (3d5/2) BEs

Calcium, (Ca)
Ca (2p3/2) BEs

Carbon, (C), in Polymers
C (1s) BEs

Cerium, (Ce)
Cesium, (Cs)
Chlorine, (Cl)
Cl (2p3/2) BEs
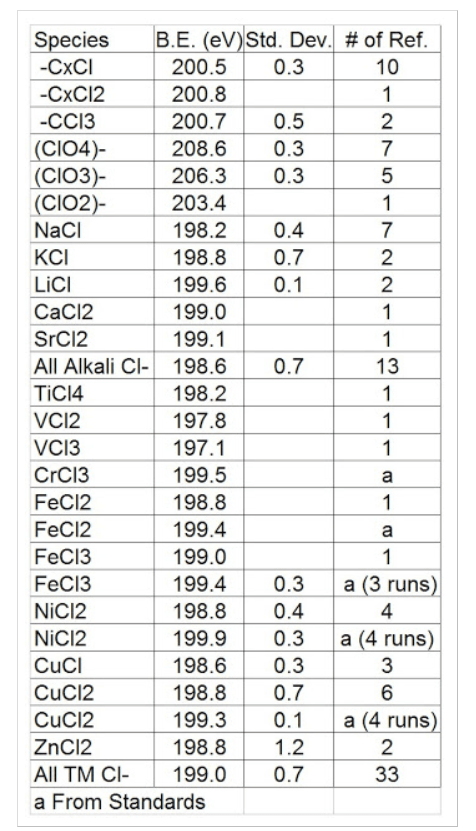
Chromium, (Cr)
Cobalt, (Co)
Copper, (Cu)
Cu (2p3/2) BEs

Copper, (Cu)
Cu (2p3/2) BEs


Dysprosium, (Dy)
Erbium, (Er)
Europium, (Eu)
Fluorine, (F)
F (1s) BEs
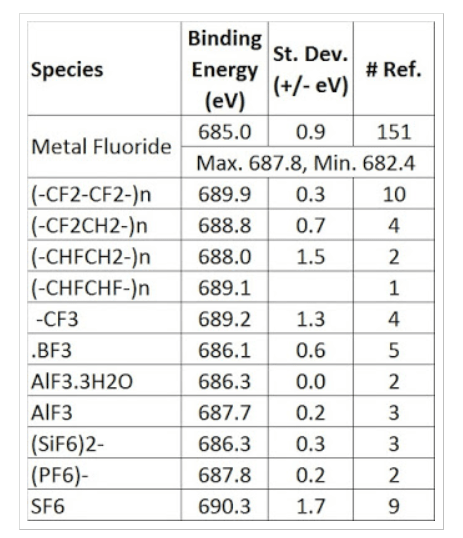
Gadolinium, (Gd)
Gallium, (Ga)
Ga (3p3/2) BEs

Ga (3d5/2) BEs

Ga (2p3/2) BEs

Germanium, (Ge)
Ge (3p3/2) BEs


Ge (3d5/2) BEs

Hafnium, (Hf)
Hf (4f7/2) BEs
Holmium, (Ho)
Indium, (In)
In (3d5/2) BEs


Iodine, (I)
I (3d5/2) BEs

Iridium, (Ir)
Ir (4f7/2) BEs

Lanthanum, (La)
Lead, (Pb)
Pb (4f7/2) BEs

Lithium, (Li)
Li (1s) BEs

Lutetium, (Lu)
Magnesium, (Mg)
Mg (1s) BEs

Manganese, (Mn)
Mercury, (Hg)
Hg (4f7/2) BEs

Molybdenum, (Mo)
Mo (3d5/2) BEs
Neodymium, (Nd)
Neon, (Ne)
Nitrogen, (N)
N (1s) BEs


Neodymium
Niobium, (Nb)
Nb (3d5/2) BEs

Nickel, (Ni)
Oxygen, (O), in Polymers
O (1s) BEs

Oxygen, (O)
O (1s) BEs


Osmium, (Os)
Palladium, (Pd)
Pd (3d5/2) BEs
Phosphorus, (P)
P (2p3/2) BEs


Platinum, (Pt)
Pt (4f7/2) BEs

Praseodymium
Rhenium, (Re)
Rhodium, (Rh)
Rh (3d5/2) BEs


Ruthenium, (Ru)
Ru (3d5/2) BEs

Samarium, (Sm)
Scandium, (Sc)
Sc (2p3/2) BEs

Selenium, (Se)
Se (3d5/2) BEs

Silicon, (Si)
Si (2p3/2) BEs

Silver, (Ag)
Ag (3d5/2) BEs

Sodium, (Na)
Na (1s) BEs

Strontium, (Sr)
Sr (3d5/2) BEs

Sulfur, (S), in Organics
S (2p3/2) BEs

Sulfur, (S), in Inorganics
S (2p3/2) BEs


Tantalum, (Ta)
Tellurium, (Te)
Te (3d5/2) BEs

Technitium, (Tc)
Terbium, (Tb)
Thallium, (Tl)
Thorium, (Th)
Thulmium, (Tm)
Tin, (Sn)
Sn (3d5/2) BEs


Titanium, (Ti)
Ti (2p3/2) BEs


Tungsten, (W)
W (4f7/2) BEs

Uranium, (U)
Vanadium, (V)
Xenon, (Xe)
Ytterbium, (Yb)
Yttrium, (Y)
Y (3d5/2) BEs

Zinc, (Zn)
Zn (2p3/2) BEs

Zirconium, (Zr)
Zr (3d5/2) BEs

Periodic Table: Select the Element to see BEs for that Element




